How Aging Affects Your Musculoskeletal System and What You Can Do About It :
As we age, our bodies undergo a series of changes, and the musculoskeletal system is no exception. The musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints, plays a crucial role in maintaining our mobility, strength, and overall quality of life. Understanding how aging affects this system and taking proactive steps to address these changes can help you maintain your independence and well-being as you grow older.
How Aging Affects the Musculoskeletal System:
1. Bone Density Loss:
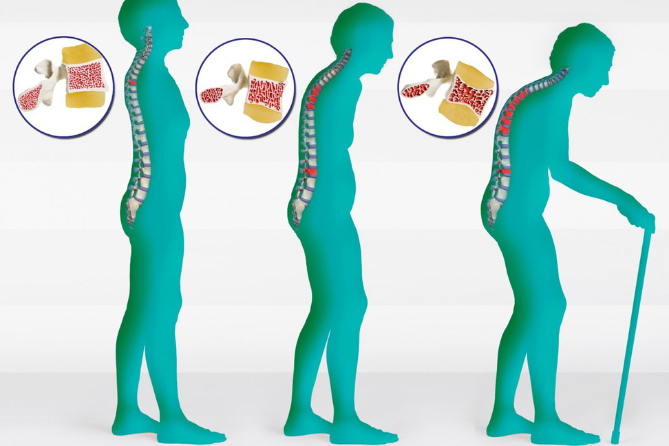
- Osteoporosis: One of the most significant age-related changes is the loss of bone density, leading to osteoporosis. Bones become thinner and more brittle, increasing the risk of fractures and breaks.
- Bone Remodeling: With age, the process of bone remodeling slows down, meaning that bone resorption (breaking down) outpaces bone formation. This imbalance contributes to reduced bone mass and strength.
2. Muscle Mass and Strength Decline:
- Sarcopenia: Age-related muscle loss, known as sarcopenia, begins around the age of 30 and accelerates after the age of 60. This condition results in decreased muscle mass and strength, impacting balance and mobility.
- Muscle Fiber Changes: The number of muscle fibers decreases with age, and the remaining fibers tend to become larger but less efficient, leading to reduced muscle function and endurance.
3. Joint Changes:
- Cartilage Degeneration: Cartilage, the smooth tissue that cushions joints wears down over time. This can lead to osteoarthritis, characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion.
- Joint Flexibility: The synovial fluid that lubricates joints decreases with age, leading to stiffer and less flexible joints.
4. Tendon and Ligament Changes:
- Tendon and Ligament Stiffness: Tendons and ligaments become stiffer and less elastic with age, reducing joint stability and increasing the risk of injuries like sprains and strains.
- Tendon Repair Slows Down: The ability of tendons and ligaments to repair and heal slows with age, making recovery from injuries more prolonged.
5. Postural Changes:
- Kyphosis: The natural curvature of the spine may increase with age, leading to a condition known as kyphosis, where the upper back becomes excessively rounded. This can affect posture and balance.
- Height Loss: Compression of the spinal discs and changes in bone density can lead to a gradual loss of height over time.

What You Can Do About It:
Maintaining the health of your musculoskeletal system as you age involves a combination of lifestyle choices, exercise, and medical care. Here’s how you can address and mitigate the effects of aging on your musculoskeletal system:
1. Engage in Regular Exercise:
- Weight-Bearing Exercises: Activities like walking, jogging, and dancing help stimulate bone formation and maintain bone density.
- Strength Training: Resistance exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, can help combat muscle loss, improve muscle strength, and enhance overall physical function.
- Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Incorporate exercises like yoga, stretching, and tai chi to improve joint flexibility, balance, and coordination, reducing the risk of falls.
2. Prioritize a Nutrient-Rich Diet:
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D to support bone health. Foods like dairy products, leafy greens, fortified cereals, and fatty fish are excellent sources.
- Protein: A sufficient protein intake is crucial for muscle maintenance and repair. Include lean meats, beans, nuts, and dairy products in your diet.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Incorporate foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and fatty fish, to support joint health and reduce inflammation.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Avoid Excessive Strain: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the stress on your joints, particularly the knees, hips, and lower back. Excess weight can exacerbate joint pain and increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Balanced Diet and Exercise: Combine a balanced diet with regular exercise to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
4. Address Joint Health:
- Manage Arthritis Symptoms: If you have arthritis, work with your healthcare provider to manage symptoms through medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
- Protect Your Joints: Use supportive devices like braces or orthotic inserts if recommended by your doctor, and avoid activities that put excessive stress on your joints.
5. Monitor Bone Health:
- Bone Density Testing: If you’re at risk for osteoporosis, discuss bone density testing with your healthcare provider to assess bone health and take preventive measures if needed.
- Regular Check-Ups: Keep up with regular medical check-ups to monitor bone health and address any issues promptly.
6. Avoid Harmful Habits:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking accelerates bone loss and impairs the healing process. Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining bone health.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can interfere with bone health and increase the risk of fractures. Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels.
7. Focus on Fall Prevention:
- Home Modifications: Make your home safer by removing tripping hazards, installing grab bars in the bathroom, and ensuring adequate lighting.
- Fall Prevention Exercises: Incorporate exercises that improve balance and coordination to reduce the risk of falls and related injuries.
For more information talk to a healthcare provider.
If you have any questions about How Aging Affects Your Musculoskeletal System, please feel free to leave a comment.
Do share this blog with your friends and family!