What is Bone Fracture?
A fracture is a medical term for a ‘broken bone’. It is a medical condition distinguished by a partial or complete break in the continuity of the bone.
Most human bones are strong and can generally withstand strong impact or forces.
However, bones break when the pressure or force applied to them is more than what they can normally withstand or if there is something wrong with them.
Bones are the skeleton of the body that allows us to interact with our surroundings. They act as attachment points for muscles that allow running, jumping, sitting, kneeling, grasping, and lifting.
As we age the bones become breakable and the force they can handle or withstand reduces. This increases the risk of fracture, immediate medical care is needed after a bone is fractured.
As serious fractures can have severe complications if not treated right away. Complications include damage to the blood vessels and infections of the bone or surrounding tissue.
Types of Fractures:
1. Transverse fracture
In a transverse fracture, the fracture line is almost perpendicular to the long axis of the bone.
Such a fracture is caused by bending force resulting from the direct blow by a moving object or by the bone striking a resistance object.

2. Oblique fracture
As the name suggests in an oblique fracture. The fracture line is oblique and makes an acute angle with the long axis of the bone.
Such a fracture is caused by bending force which in addition has a component along the long axis of the bone.

3. Spiral fracture
In a spiral fracture, the fracture line runs spirally in more than one plane.
Such a fractured is caused by an indirect rotational or twisting force with increasing energy transfer the spiral fractures may have butterfly fragments.

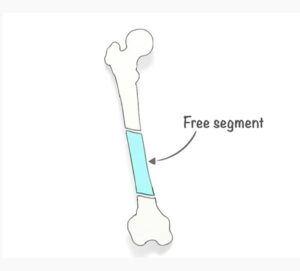
4. Segmental fracture
In a segmental fracture there are two fractures in one bone but at different levels leading to a free segment in between.
5. Impacted fracture
A fracture where one fragment of bone goes into another. Bone fragments are driven into each other.

6. Aulsion fracture
A fracture where a fragment of bone is separated or pulled off by a ligament or tendon.

7. Complete fracture
A fracture in which the bone breaks completely.
Types of complete fracture are:
1. Comminuted fracture
Bone fragments break into three or more pieces.

2. Single fracture
Bone fragments break in one place into two pieces.

3. Non-Displaced fracture
Bone fragments break into pieces and stay in their normal alignment.

4. Displaced fracture
Bone fragment breaks into pieces that shift off their normal alignment.

5. Incomplete fracture
The bone doesn’t break completely. Incomplete fractures are more common in children. Whose bones are softer and more elastic.

Types of incomplete fractures are:
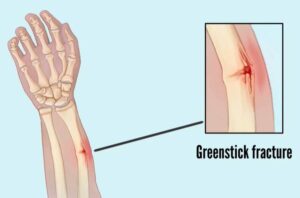
1. Greenstick fracture
The bone partly fractures on one side while the rest of the bone is bent.
3. Hairline fracture
A partial fracture of the bone usually in a thin crack.
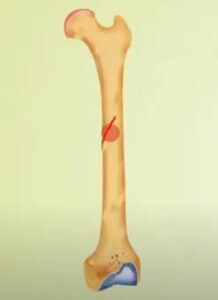
4. Torus (buckle) fracture
The bone is broken on one side and a bump or raised buckle grows on the other side.

Types of fracture Displacement:
The fracture displacement is described in terms of change in length, angulation, rotation, and translation.
Change in Length
Let’s see how a displaced fracture cause’s change in the limb length. Apposition is the amount of end-to-end contact of the fracture fragments.



Bayonet apposition means overlap of the fracture fragments in the longitudinal axis here the bone ends have no contact and have slipped past each other the fracture is called “off-ended”. This results in a shortening of the limb length.
The bayonet apposition gets its name from the bayonet rifle.
Excessive traction may result in the opposite deformity leading to distraction

Angulation
Angulation is described by the reference to the apex of the fracture in the coronal plane a fracture with displacement of the distal fragments towards the midline with its apex pointing laterally is said to be in Varus.

A fracture with its displacement of the distal fragment away from the midline with the apex pointing towards the midline is said to be in Valgus.

Sagittal Plane
In the sagittal plane, a fracture with its apex pointing posteriorly is said to have posterior angulation or to line extension.

Finally, where the apex points anteriorly the fracture has anterior angulation or lies inflection.
Rotation
A fracture may be rotated internally or externally. This is judged by the appearance of the two bone ends and the position of the distal part of the limb clinically.

Translation
Translation occurs when the fracture surfaces have shifted sideways relative to each other depending on the position of the distal fragment.

A fracture may be translated medially, laterally, anteriorly, posteriorly, or even a combination of these.

Relationship with External Environment:
On the basis of relationship with the external environment. Fractures can be classified as either closed or open.
Closed fracture
A closed fracture is a fracture not communicating with the external environment that is the overlying skin and soft tissues are intact.

Open fracture
Whereas a fracture with a break in the overlying skin and the soft tissues leading to the fracture communicating with the external environment is called an open fracture.

With an open fracture, there is a high risk of infection.
Etiology of fracture:
1. Traumatic fracture
Traumatic fracture is a fracture of a bone following direct or indirect violence.
A normal healthy bone breaks only when it is subjected to excessive force.
Hence, these fractures are caused by the action of an abnormal excessive force on a normal healthy bone.

Examples of traumatic fractures include fractures caused by a fall, road traffic accident, fight, etc.
2. Pathological fracture
This type is a result of an underlying condition or disease that has already weakened the bone. Such as cancer or osteoporosis.

3. Stress fracture
Stress or fatigue fracture results from the cyclical application of the normal forces in excessive frequency to the normal bone of a healthy patient leading to a break in bony trabeculae.
The classic examples include second metatarsal fractures of army recruits popularly known as the March fracture.
The fracture of the navicular bone in athletes. Stress fractures are typically seen in military personals, athletes, or dancers. When the intensity of the exercise is significantly increased from the baseline.

Quantum of force:
On the basis of the quantum of force causing the fracture. The fractures can be classified into high and low-velocity injuries.
A high-velocity injury is caused by severe trauma force as in a road traffic accident. These fractures are associated with severe soft tissue injury with extensive devascularisation of the fracture ends.
These are usually more complex fractures and difficult to treat. Such fractures are often unstable and slow to heal.
The low-velocity injuries are caused by mild trauma force as in a fall. There is little associated soft tissue injury.
Symptoms:
- Intense pain in the sight of the injury.
- Swelling, bruising, and redness in the injured area.
- Deformity in the injured area.
- Difficulty moving or supporting the weight with the affected area.
Causes of Fractures:
- Falls, direct blows, or strikes to the body.
- Injuries from sports osteoporosis repetitive forces caused by running, automobile accidents.
- Risk factors may include being old, smoking, alcoholism, and use of corticosteroids being physically inactive.
Diagnosis:
The doctor will ask about symptoms. Examine the injury and look for other injuries that may have occurred.
The American Academy of orthopaedic surgeons provides that x-rays are the most common method of diagnosing a fracture.
They help in visualizing the bone and revealing breaks and other signs of damage as well as in determining the location and type of the fracture.
In cases where x-ray alone is insufficient CT scan or MRI may be used.
Treatment:
Treatment options depend on the type and location of the fracture.
The first goal of treatment is to try to put the broken pieces back into their proper position and stabilize them as they heal.
Pieces of broken bones should be kept immobile until they are together.
A cast may be used to stabilize the broken bone. The cast may be made of fiber or glass and it will help stabilizer the injured area and keep broken pieces compact until they heal.
Complex injuries may require surgery.
Conclusion:
This was all about types of fractures and their mechanisms.
So, if you have gained knowledge from this article, so please share this article and spread the knowledge with your friends and family.
Or maybe if I didn’t mention the fracture type which you wanted to read.
Either way, let me know by leaving a comment below right now.